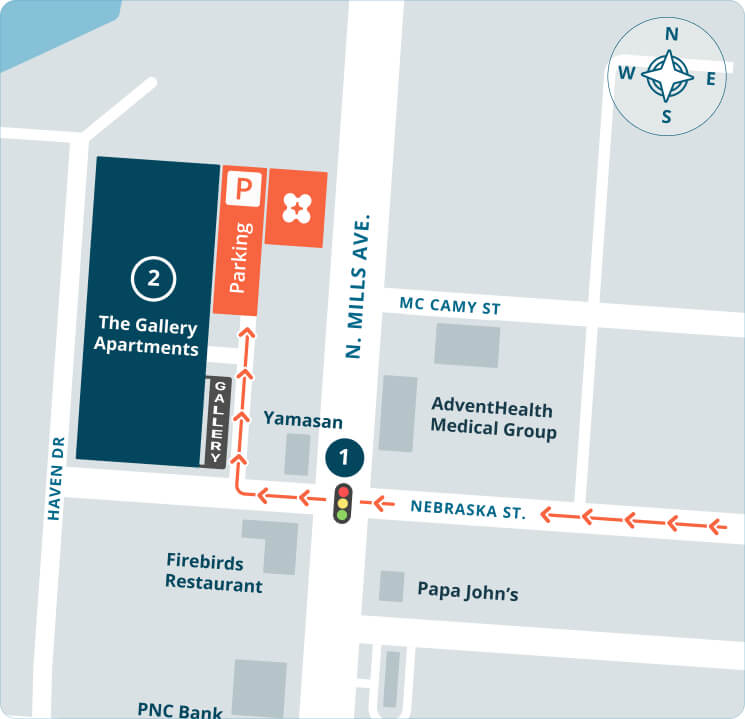
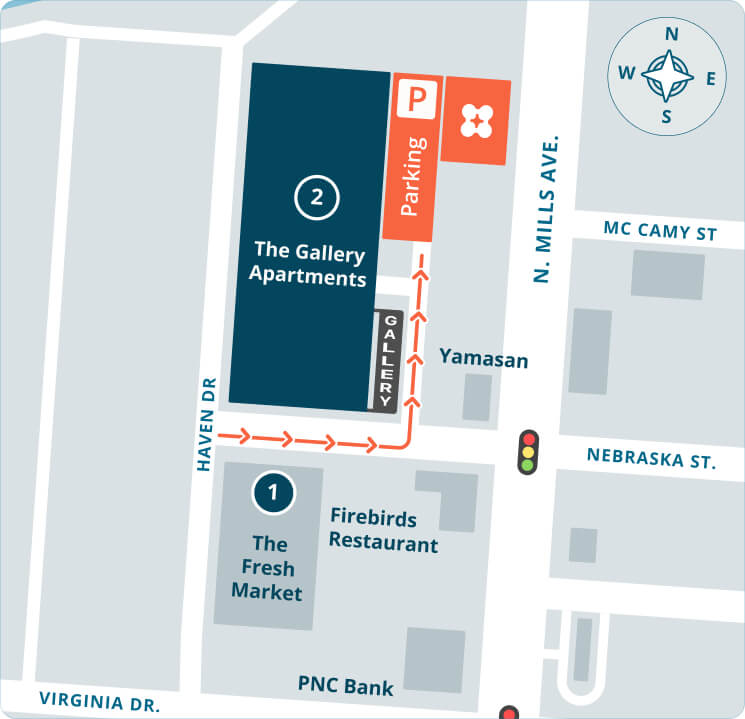
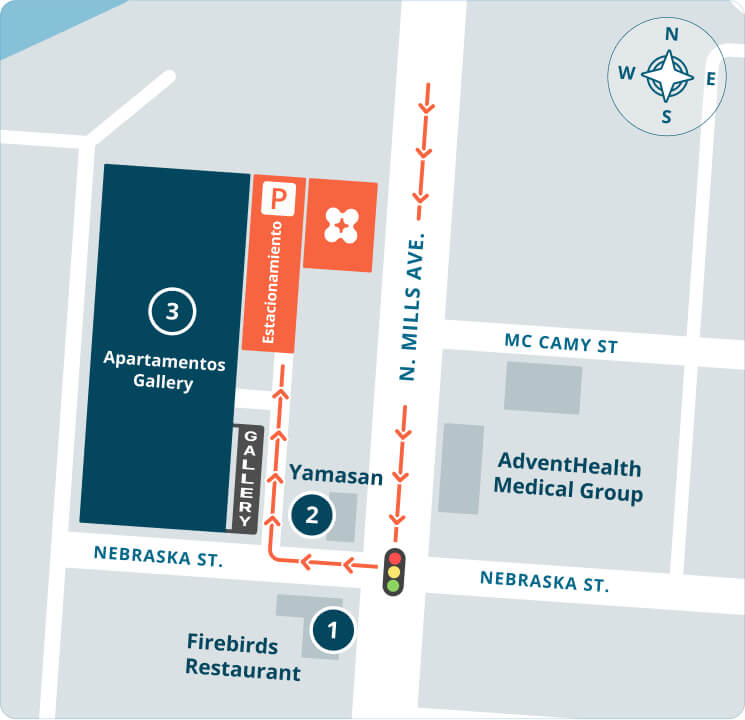
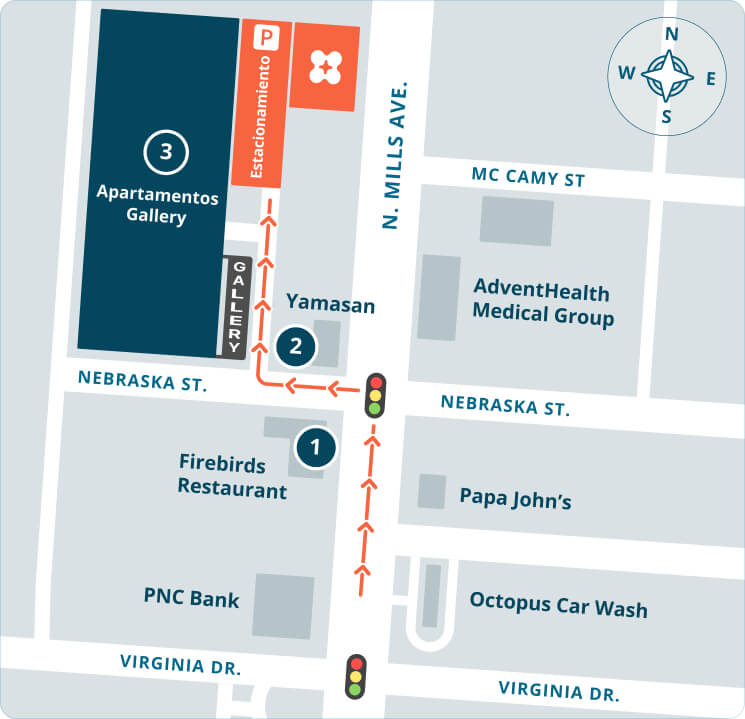
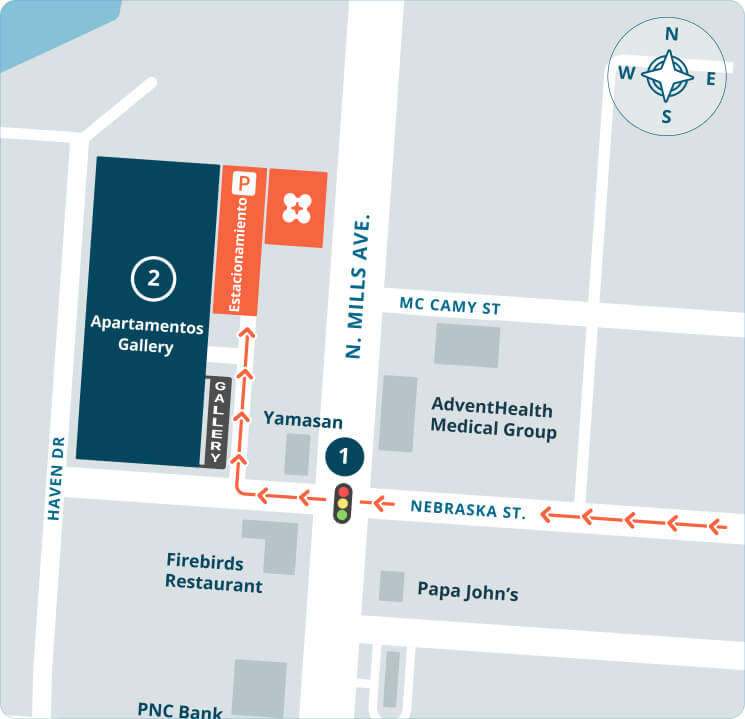
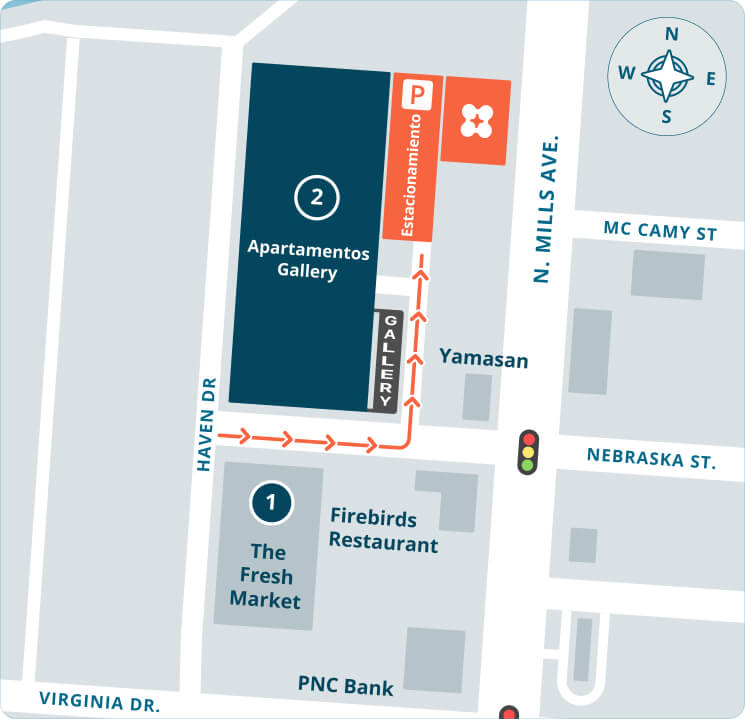
Refer a friend
Refer a friend or family member to join research study today and you will receive a $55 Visa gift card when they enroll.
Pick a friend or a family member who is new to Charter Research.
Fill out the form below.
Fill Out The Form
Study
“Healthy” Alzheimer’s Study
Does Alzheimer's disease run in your family?
A study for healthy individuals.
This study examines whether a new drug may help to slow or prevent the onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in those with elevated risk of developing the disease.
Amyloid plaque—an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease—can begin building up in the brain at least 10 years before the onset of the disease. Because of this, there is a need for a treatment that delays cognitive and functional decline, prevents dementia, and allows individuals to remain independent longer.
This study will evaluate the effectiveness of the investigational drug, an antibody that removes amyloid plaque. This potential treatment, utilizing a subcutaneous injection, could possibly represent an important treatment option for individuals with early Alzheimer’s, as well as those who are healthy, but have a family history of AD.
If you’re worried that your memory might start fading, then joining an Alzheimer’s prevention study might be a great option for you. It might just help future generations, too.
Who is eligible?
You may qualify for this study if:
- You are 65-80 years of age.
- You have a reliable study partner.
- You will be available for the duration of the study and are willing to follow study procedures.
Sign Up
Schedule Your Assessment
Sign up for an initial assessment (called a “prescreen”), and we'll give you a call. One of our professional medical staff will answer your questions and give you more information about Charter Research prior to an in-office visit.